Khouloud Razki
Conference 2024 Poster
Poster Title
Factors Influencing Mental Health Patient Satisfaction : Insights from a study of 200 Patients
Authors and Affiliations
Khouloud Razki1, Sofiene Ben Aissa2, Chaima Najjar2, Yosra Zgueb1
1. Department of psychiatry A, Razi hospital, Tunisia.
2. Department os psychiatry D, Razi hospital, Tunisia.
Abstract
Background
The assessment of user satisfaction has recently emerged as a consistently emphasized objective and a major challenge for public health services. It provides feedback to the healthcare system following its care services. Although it is commonly accepted and widely used in healthcare facilities, patient satisfaction remains equivocal and difficult to define.
The aim of our study is to evaluate patient satisfaction with the care received in a psychiatric setting.
Methods
This is a cross-sectional descriptive study that took place over a period of five months from April to August 2019 in psychiatric service at Razi Hospital in Tunisia. Data collection was initially done from patient medical records and then verified and completed during direct interviews using a pre-established information form consisting of 29 questions including socio-demographic data and clinical data concerning the patient’s mental disorder. We designed and validated a questionnaire consisting of 28 items to evaluate patient satisfaction with the quality of care received in a psychiatric setting.
Results
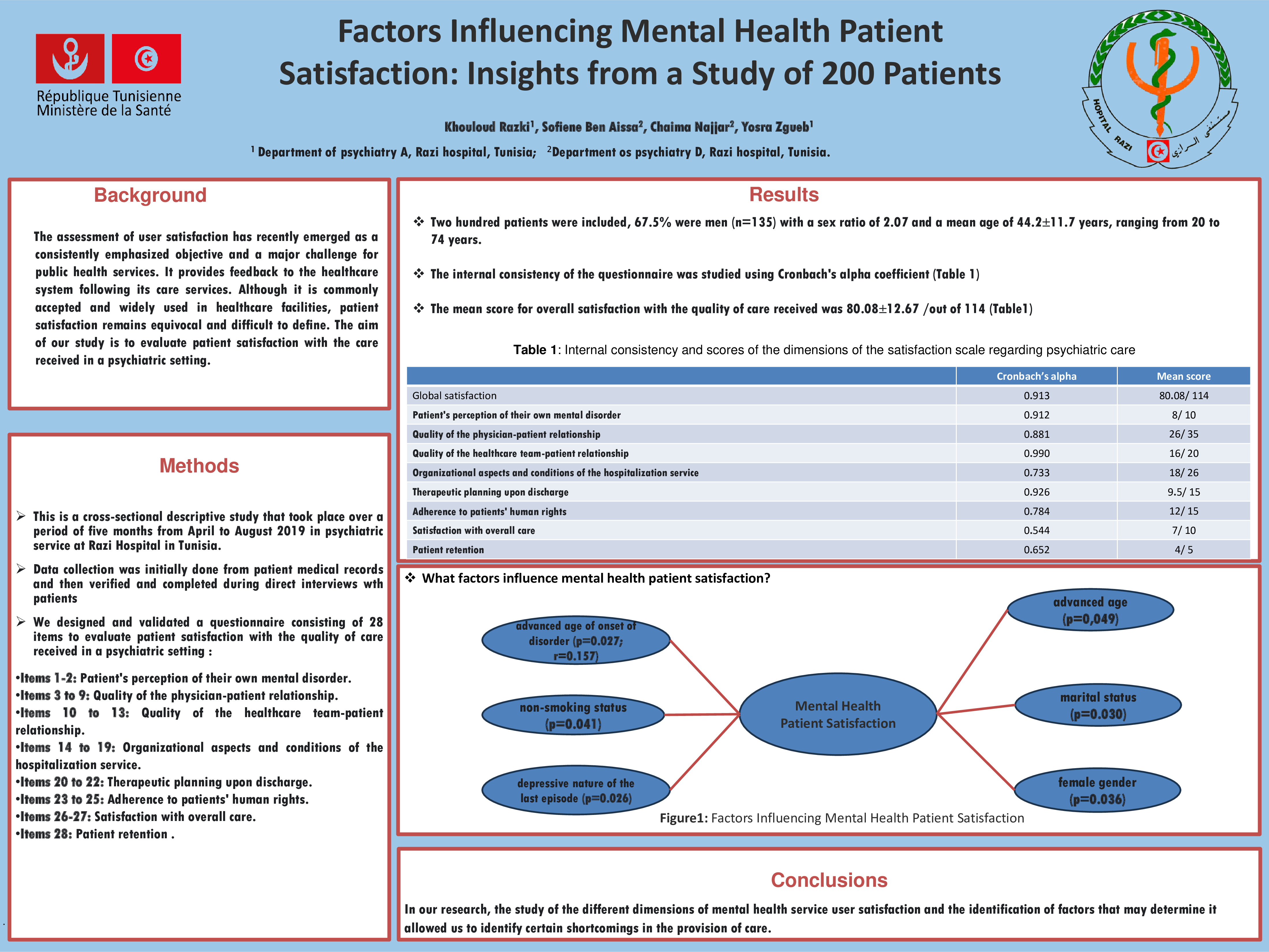
Two hundred patients were included, 67.5% were men (n=135) with a sex ratio of 2.07 and a mean age of 44.2±11.7 years, ranging from 20 to 74 years.
The internal consistency of the questionnaire was studied using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient. The results obtained for each dimension were higher than 0.50. The overall alpha coefficient was 0.913.
The mean score for overall satisfaction with the quality of care received was 80.08±12.67 (a score out of 140), of which 51.5% of patients scored higher than or equal to this score.
We found six determinants that were statistically significantly associated with overall satisfaction: advanced age of the patient (p=0.049), female gender (p=0.036), marital status (married subjects) (p=0.030), non-smoking status (p=0.041), advanced age of onset of psychiatric disorder (p=0.027; r=0.157), and depressive nature of the last thymic episode (p=0.026).
Conclusions
In our research, the study of the different dimensions of mental health service user satisfaction and the identification of factors that may determine it allowed us to identify certain shortcomings in the provision of care. The reform of the “Razi” psychiatric establishment is a priority in the process of optimizing the quality of care. Moreover, achieving quality requires the mobilization of all stakeholders, including healthcare professionals, administration, and the Ministry of Public Health, around objectives through real and effective collective involvement.

Leave A Comment